uses of concave and convex lens
In this extensive exploration of concave and convex lenses, we will delve into their properties, functions, and various applications across different fields. We will discuss the principles of optics, the anatomy of lenses, and provide detailed examples of how these lenses are used in everyday life, science, technology, and various industries you will have a comprehensive understanding of concave and convex lenses and their significance in our world.
Introduction
Lenses are fundamental optical components that play a crucial role in shaping the way we perceive the world around us. These transparent pieces of glass or other transparent materials have been used for centuries to manipulate and control the passage of light, allowing us to magnify, reduce, or alter the direction of light rays. Lenses come in various shapes and sizes, but two of the most common types are concave and convex lenses.
I. Basics of Optics
Before we dive into the specific uses of concave and convex lenses, it's important to establish a fundamental understanding of optics and how lenses interact with light.
A. Principles of Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that deals with the behavior of light, including its reflection, refraction, dispersion, and polarization. The behavior of light can be described using two main principles: the wave theory of light and the ray theory of light.
Wave Theory of Light: According to this theory, light is a form of electromagnetic radiation composed of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. Light waves travel in straight lines and can undergo various interactions with matter, including reflection and refraction.
Ray Theory of Light: The ray theory simplifies the behavior of light by representing it as rays that travel in straight lines. It is particularly useful for understanding how light interacts with lenses and other optical devices.
B. Refraction and Lenses
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes from one medium into another of different optical density. Lenses are optical devices designed to exploit the phenomenon of refraction to manipulate light. They consist of transparent material with curved surfaces.
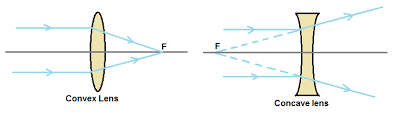
Convex Lens: A convex lens is thicker in the center than at the edges and causes parallel rays of light to converge, or come together, at a single point known as the focal point. This is due to the fact that the convex surface of the lens causes the light rays to bend inward as they pass through it.
Concave Lens: A concave lens, on the other hand, is thinner in the center and causes parallel rays of light to diverge, or spread apart. The point from which the diverging rays appear to originate when extended backward is called the focal point.
II. Concave Lens
Now that we have a foundational understanding of optics and lenses, let's explore the uses of concave lenses.
A. Vision Correction
Myopia (Nearsightedness): One of the most common applications of concave lenses is in vision correction. Myopia, or nearsightedness, is a condition where distant objects appear blurry because the eyeball is too long or the cornea is too curved. Concave lenses are used to diverge incoming light rays before they enter the eye, allowing the image to focus properly on the retina.
Presbyopia: Concave lenses can also be used to correct presbyopia, a condition where the eye's natural lens loses flexibility with age, making it difficult to focus on close-up objects. These lenses help restore the ability to focus on near objects by providing additional divergence to incoming light.
B. Microscopes and Telescopes
Microscopes: Concave lenses are used in some microscope systems to further magnify the image produced by the objective lens. By combining a concave lens with the objective lens, it is possible to correct for certain aberrations and enhance the overall image quality.
Telescopes: In astronomical telescopes, concave lenses are sometimes employed as field lenses or eyepieces. These lenses help to magnify the image formed by the primary lens or mirror, allowing astronomers to observe distant celestial objects more closely.
C. Diving Masks
Concave lenses are incorporated into diving masks to correct underwater vision. When submerged, the light entering the mask is refracted differently due to the change in medium (from air to water). The concave lenses counteract this effect, ensuring that divers can see clearly underwater.
D. Ophthalmic Instruments
Concave lenses find use in ophthalmic instruments such as retinoscopes and keratometers. Retinoscopes are used by eye care professionals to measure a patient's refractive error, and keratometers help assess the curvature of the cornea, aiding in the fitting of contact lenses and the planning of refractive surgery.
E. Photography
In photography, concave lenses are sometimes employed to correct certain aberrations in camera lenses. These aberrations, such as chromatic aberration and distortion, can be minimized or eliminated by using specially designed concave lens elements within the camera lens.
III. Convex Lens
Now, let's turn our attention to the diverse applications of convex lenses.
A. Vision Enhancement
Hypermetropia (Farsightedness): Convex lenses are commonly used to correct hypermetropia, or farsightedness. In hypermetropic individuals, distant objects are seen more clearly than nearby ones due to an eyeball that is too short or a cornea that is too flat. Convex lenses converge incoming light rays, helping to focus them properly on the retina.
Reading Glasses: Many people require convex lenses, often in the form of reading glasses, as they age and develop presbyopia. These lenses make it easier to focus on close-up objects by converging light rays before they enter the eye.
B. Magnifying Glasses
Convex lenses are integral components of magnifying glasses, loupes, and magnifiers. These lenses are used to enlarge and clarify small or fine details, making them indispensable tools in fields like jewelry making, watch repair, and printing.
C. Cameras and Projectors
Cameras: Convex lenses are at the heart of camera lenses. They converge light rays from the scene being photographed, creating a sharp and focused image on the camera's sensor or film. Various types of camera lenses, including wide-angle and zoom lenses, use convex elements to achieve specific optical effects.
Projectors: Convex lenses are crucial in projectors to focus and enlarge the image from a small source (such as a slide or digital image) onto a larger screen. They can also be used to correct image distortions.
D. Eyepieces in Optical Instruments
Convex lenses are commonly found in eyepieces of optical instruments like binoculars, microscopes, and telescopes. They serve to magnify the image formed by the objective lens or mirror, allowing for detailed observations of distant or small objects.
E. Optical Instruments for Measurement and Inspection
Convex lenses are used in various optical instruments for measurement and inspection purposes. Examples include autocollimators, theodolites, and profile projectors, where they help with precise alignment, angle measurement, and image magnification.
F. Solar Concentrators
Convex lenses are used in solar concentrators, which focus sunlight onto a small area to generate high temperatures. These concentrated solar energy systems are used in solar


I think your content is going good day by day but you should use a beautiful template for your blog and focus on one content. sometimes you post one content but at the other time you changed your content 🤔
ReplyDelete